The Enneagram system is a fascinating and insightful psychological tool that provides a rich framework for understanding human personality. Rooted in ancient wisdom traditions and brought into the modern age with psychological insights, the Enneagram outlines nine distinct personality types.
Each type has its own unique set of characteristics, motivations, fears, and desires. This system goes beyond mere categorization; it offers a deep understanding of individual behavior patterns and how different types interact.
By exploring the Enneagram, individuals can gain valuable insights into their behaviors and motivations, leading to personal growth, improved relationships, and increased empathy towards others.
Key Takeaways from the Article
- The Enneagram as a Tool for Personal Growth: The Enneagram is more than just a personality typing system; it’s a comprehensive guide for self-understanding and personal development. It allows individuals to explore the depths of their personality traits, strengths, and weaknesses in a structured manner.
- Understanding Core Motivations: One of the core benefits of engaging with the Enneagram is its ability to reveal the underlying motivations behind one’s behaviors and attitudes. This insight can lead to greater empathy for oneself and a deeper understanding of others.
- Dynamic Nature of Personalities: The Enneagram underscores the fluidity and complexity of human identity. It acknowledges that individuals can exhibit characteristics of other types under different circumstances, challenging the notion of a fixed personality.
- Practical Applications in Workplace Settings: Beyond personal development, the Enneagram is an effective tool for enhancing teamwork, leadership, and communication in professional environments. Understanding the diverse personality types can lead to more harmonious and productive work relationships.
- Journey Towards Self-Discovery: Engaging with the Enneagram is described as a lifelong journey that offers continuous learning and personal growth opportunities. It invites individuals to remain open to self-exploration and to use their newfound insights to foster more fulfilling lives and relationships.
BPT (Best Personality Tests) emerges as an exceptional solution for those interested in taking the Enneagram test to facilitate their personal growth and self-discovery journeys. This platform offers an easy-to-navigate interface and a comprehensive assessment, making it accessible for both beginners and those already familiar with the Enneagram.
By utilizing BPT, individuals can gain insights into their core motivations, personality dynamics, and areas for development, laying the groundwork for a more profound understanding of oneself and improving interactions with others.
What is the Enneagram of Personality?
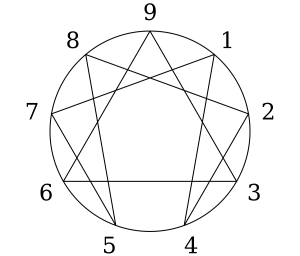
The Enneagram of Personality is a dynamic system that encapsulates nine interrelated personality types, offering a 360-degree overview of human psychology
Each type is designated by a number (One through Nine) and is characterized by a distinct worldview and an underlying motivation that profoundly influences a person’s thoughts, feelings, and actions.
Unlike static personality models, the Enneagram views individuals as evolving, with the potential to access qualities of all nine types, creating a more nuanced profile of human personality.
The Core Types
At the Heart of the Enneagram are the nine core types, further divided into three intelligence centers: intuitive, feeling, and thinking. Each center focuses on a primary aspect of human experience.
The instinctive center (Types Eight, Nine, and One) deals with control issues and resistance to change. The feeling center (Types Two, Three, and Four) addresses issues of identity and self-worth.
Finally, the thinking center (Types Five, Six, and Seven) revolves around security and coping strategies.
Wings and Paths of Integration and Disintegration
An essential aspect of the Enneagram of Personality is the concept of wings and the paths of integration and disintegration. Wings are the neighboring types on each side of a person’s core type and can influence their primary personality.
For example, a Type Four could have a “Three wing” (4w3) or a “Five wing” (4w5), contributing additional layers to their personality. Furthermore, each type has integration (growth) and disintegration (stress) paths, indicating how a person’s behavior changes during different life phases.
These paths illustrate the fluidity of the Enneagram and its ability to depict complex human behaviors.
Applications in Daily Life
Understanding the Enneagram can profoundly impact various areas of one’s life. In personal development, it facilitates self-awareness and uncovers blind spots, leading to more authentic interactions.
It also enhances relationships by fostering more profound empathy and understanding between differing personality types. Professionally, the Enneagram can be a tool for improving workplace dynamics and leadership styles, as it encourages effective communication and acknowledges diverse perspectives.
The Enneagram of Personality is not merely a tool for categorization but a map for personal growth and understanding. Its comprehensive approach to understanding human complexity makes it a valuable asset for anyone seeking to deepen their understanding of themselves and others.
By studying the Enneagram, individuals can navigate the intricacies of personality with more grace, leading to more prosperous, more fulfilling lives.
How Does the Enneagram Work?
The Enneagram operates on the principle that understanding your core personality type can unveil key motivations, fears, and behaviors that drive your actions. Imagine it as a mirror reflecting not just who you are on the surface but the intricate web of traits beneath.
This depth of insight encourages a profound inner exploration, enabling individuals to confront aspects of themselves they may not have recognized or understood.
Each of the nine core types of the Enneagram has distinct characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses. Recognizing your core type is like finding the base camp for your personal development journey.
From here, you can start understanding why you react to certain situations in specific ways and how you relate to the people around you. It’s akin to uncovering the fundamental programming influencing your perception of the world and your interactions.
Wings add nuance to the Enneagram’s personality portraits. They are the adjacent types on either side of your core type and can significantly influence your overall personality. Think of wings as the spices that flavor the main dish – your core type.
Some individuals may find that one wing is more dominant, adding a unique blend of traits to their personality recipe. This concept illustrates that human nature is not rigid but fluid, with layers that contribute to our complexity.
The Enneagram illustrates how personalities evolve or regress undergrowth and stress through paths of integration and disintegration. Visualize a road map where certain conditions lead you to higher self-awareness and others to more challenging behaviors.
This dynamism underscores the Enneagram’s value in personal development, guiding life’s ups and downs with greater resilience and understanding.
Beyond self-exploration, the Enneagram’s insights into human behavior enhance relationships and professional dynamics. Understanding the diverse lenses through which we view the world can foster more empathetic and effective interactions.
This translates to a collaborative environment where diverse strengths are valued, and communication barriers are minimized in the workplace. Whether personal or professional, the Enneagram empowers individuals to build deeper connections and work together more harmoniously.
The Enneagram’s comprehensive approach to deciphering human behavior makes it more than a typology system – it’s a roadmap to personal growth and better interpersonal relationships.
Its structure emphasizes the complexity and fluidity of human nature, encouraging an ongoing process of self-discovery and improvement.
How are Enneagram Figures Determined?
The foundation of determining one’s Enneagram type lies in understanding the core motivations that drive one’s behaviors. These motivations relate to deep-seated desires and fears, such as the desire for security, love, and autonomy, as well as concerns about worthlessness, being unlovable, or incompetence.
By introspectively examining what consistently drives one’s actions, individuals can start to narrow down their Enneagram type. It’s crucial to approach this process honestly and openly, as idealized versions of ourselves can often cloud self-perception.
Once the primary Enneagram type is identified, further nuances are explored through “wings” and “instinctual variants.” Wings are the adjacent types on either side of your primary type and can significantly influence your personality.
For example, if you’re a Type 2, your wings could be Type 1 or Type 3, adding layers to your core type.
Instinctual Variants, however, reflect your instinctual needs and priorities, such as self-preservation, social interactions, or one-to-one relationships. These aspects further refine your understanding of your Enneagram figure, offering a more comprehensive view of your personality.
Feedback from friends, family, and colleagues can provide valuable insights into your behaviors and motivations. Often, others can observe aspects of our personality that we might overlook or underestimate.
Engaging in conversations about how others perceive your reactions, decision-making processes, and relationship styles can offer clues to your Enneagram type.
However, it’s essential to remember that the final determination should resonate with your personal experiences and core motivations.
Various self-assessment tools and questionnaires are available to determine your Enneagram type. These resources typically involve questions designed to probe your motivations, fears, and behaviors. While these tools can be handy, they should not be used in isolation.
The complexity of human personality means that no test can definitively determine your Enneagram type without your introspection and judgment.
Determining your Enneagram type is not a one-time event but a continuous reflection and exploration process. As you grow and your circumstances change, you may find that different aspects of your personality come to the fore. The Enneagram is a dynamic tool accommodating the fluid nature of human personality.
Regularly revisiting your motivations, fears, and behaviors in light of new experiences can provide deeper insights into your type and promote ongoing personal development.
The Nine Types of Enneagram Personality Explanation
Here are the nine types of Enneagram personality:
Type A’s sense of right and wrong drives one’s personality. They are conscientious, responsible workers focused on improvement and integrity in themselves and the world around them.
They are motivated by the need to live correctly, including improving themselves and the world. They can struggle with anger and resentment when reality falls short of their ideals.
Twos are caring, interpersonal types who seek to be loved and needed. They are empathetic, sincere, and warm-hearted. Their primary motivation is to feel loved, which they try to achieve by directly helping others.
Twos need to be needed and thus focus on people-pleasing and self-sacrifice, sometimes leading to ignoring their needs.
The Achiever, or Type Three, focuses on success and validation through achievements. They are adaptable, excelling, driven, and image-conscious, desiring to appear successful and valuable.
Threes work hard to meet their goals and gain recognition but may struggle with being out of touch with their true feelings and identity beneath the veneer of success.
Type Fours are self-aware, sensitive, and reserved. They are emotionally honest, creative, and personal but can also be moody and self-conscious.
With a deep fear of being insignificant, Fours are motivated by the need to be unique and express themselves. Their challenge lies in overcoming feelings of envy and inadequacy.
Type Five personalities are intense, cerebral, and wise. They engage with the world by observing and understanding it, often becoming innovative and visionary.
Fives are motivated by the desire to gain knowledge and competence. However, their need for independence and fear of being overwhelmed by others’ needs can lead to detachment and isolation.
Reflecting on personal motivations, fears, and behaviors is crucial to exploring these types. Each Enneagram type has its distinct pathway for growth, and understanding your type can be a powerful guide in personal development.
This type is characterized by their strong sense of loyalty and commitment. They value security and stability, often seeking out relationships and communities where they feel supported and protected.
However, this can also lead to a tendency towards anxiety and overthinking as they try to anticipate potential threats or challenges. The need for certainty drives sixes and may struggle with making decisions or taking risks.
To grow, Sixes must learn to trust themselves and others more fully, rather than constantly seeking reassurance from external sources. Developing self-confidence and taking calculated risks can help them break free from fear-based patterns and embrace their inner strength.
Sevens are known for their cheerful, optimistic outlook on life. They are spontaneous, energetic, and easily excitable, always looking for new experiences and opportunities. Driven by the need to avoid pain and discomfort, they seek pleasure and novelty wherever they can find it.
While this makes them fun-loving and adventurous, it can also lead to a fear of missing out or becoming bored. Sevens may struggle with commitment or sticking to long-term goals as they constantly seek out new distractions.
To grow, Sevens must learn to sit with discomfort and embrace moments of stillness rather than constantly chasing after excitement. Developing patience and focus can help them cultivate deeper relationships and accomplish their goals more intentionally.
Eights are strong-willed, assertive individuals who value independence and strength. They are natural leaders driven by a desire for control and the need to protect themselves and others. Eights can be aggressive and have a strong sense of justice, often standing up against injustice and advocating for the underdog.
However, their intensity and tendency towards anger can sometimes lead to conflicts with others. To grow, Eights must learn to balance their assertiveness with vulnerability, allowing them to open up emotionally instead of always being defensive.
Nines are easygoing individuals who value harmony and peace above all else. They avoid conflict at all costs and prioritize maintaining a calm environment. Nines are great mediators and empathetic listeners, making them excellent friends and partners.
However, this desire for peace can also lead to Nines neglecting their own needs and desires to keep the peace with others. They may struggle with asserting themselves and making decisions, as they want to please everyone around them.
To grow, Nines must learn to prioritize their own needs and boundaries and not always sacrifice themselves for the sake of harmony. They must also work on recognizing and expressing their emotions instead of suppressing them to avoid conflict.
The Centers
The Enneagram introduces the concept of three centers of intelligence and perception: the Head, the Heart, and the Body centers. Each center encompasses three Enneagram types, revealing how different personalities rely on thinking, feeling, or instinctual approaches to navigating the world.
The Head Center, encompassing Types Five, Six, and Seven, prioritizes thinking and analysis. Individuals within this center are often driven by a need to understand the environment, plan for the future, and seek certainty.
Fives are the epitome of the desire for knowledge; Sixes exemplify the need for security and support, while Sevens display a quest for variety and excitement. Despite their differences, a common thread among these types is their reliance on intellect to process their experiences and decisions.
The Heart Center includes Types Two, Three, and Four, focusing on emotions, identity, and self-image. Twos are motivated by the need to be loved and appreciated, Threes seek validation through achievements, and Fours desire to be unique and express individuality.
Each type in this center struggles with self-esteem and identity, heavily influenced by their feelings and how they believe others perceive them.
Types Eight, Nine, and One fall under the Body center and are characterized by instinctual and gut reactions to their surroundings.
Eights are protectors, using their strength to control their environment; Nines seek peace and harmony, often neglecting their desires for the sake of others; and Ones aim for perfection, guided by a strong sense of right and wrong.
For these types, physical sensations and gut instincts play a crucial role in decision-making and how they interact with the world.
Each center and the types within it offer unique insights into human behavior, motivations, and growth paths. Understanding the centers gives us a broader perspective on the Enneagram system and a deeper comprehension of our own and others’ actions and reactions.
Engaging with these concepts encourages self-discovery and a more compassionate and empathetic view of those around us.
Wings
The Enneagram teaches that no personality type exists in isolation. Each type is influenced by its adjacent types, known as “wings,” which add complexity and depth to an individual’s core type.
For instance, a Type Two (The Helper) might have a One wing (2w1) or a Three wing (2w3), meaning they exhibit secondary characteristics of either the One or the Three.
These wings help to create a more nuanced understanding of each type, highlighting the fluidity and spectrum of human behavior rather than boxing individuals into a single category.
Wings are significant because they influence how a person’s core personality type is expressed. For example, a Type Three with a Two wing (3w2) would probably be more publicly engaging and people-oriented than a Type Three with a Four wing (3w4), who might display more introspection and a focus on uniqueness.
Understanding one’s wings can provide insight into motivations, behavior, preferences, and even one’s personal growth paths.
Each center of the Enneagram – Heart, Head, and Body – uniquely interacts with wings. Wings can either strengthen the characteristics of a center or balance them by introducing aspects of the adjacent centers.
For example, a Nine (Body center) with One wing (also Body center) may focus more on right and wrong and a heightened sense of justice. Contrastingly, a Nine with an Eight wing introduces the dynamism and assertiveness of the Body center to the peace-seeking Nine, creating a blend of traits that encourages peace and action.
Understanding and integrating one’s wings is critical to personal development within the Enneagram framework. Recognizing the influence of wings allows individuals to lean into these secondary traits, fostering balance and wholeness.
For instance, a Four (Heart center) could harness its Three wings to channel its deep emotions and creativity into productive, goal-oriented activities. Diving into the unique characteristics of one’s wings can unlock new areas for growth, self-awareness, and fulfillment.
The concept of wings adds richness to the Enneagram’s typology, reminding us that our personalities are multifaceted and that growth lies in exploring and integrating the full spectrum of our traits.
Acknowledging and understanding the interplay between our core type and wings opens pathways to more nuanced self-awareness and deeper connections with others.
Wings encourage us to see beyond our primary type and explore the diverse aspects of our identity, fostering a holistic approach to our personal and spiritual development.
Arrows and Connecting Lines
The Enneagram also introduces the concept of arrows and connecting lines, which add another layer of depth to understanding personality dynamics. Arrows signify the direction of integration (growth) or disintegration (stress) for each Enneagram type.
Under stress, individuals tend to exhibit traits of a different kind in a way that is not conducive to their well-being. Conversely, when growing and integrating, they move towards another type, adopting its healthy aspects.
Each Enneagram type has a specific direction of disintegration or stress, symbolized by a line connecting their primary type to another on the Enneagram diagram.
For instance, under stress, a Type Two (the Helper) might exhibit qualities of Type Eight (the Challenger), such as becoming more controlling or aggressive. This shift is not about changing types but rather integrating aspects of a different kind in less healthy ways.
Understanding these dynamics can alert individuals to their stress responses and encourage them to seek healthier coping mechanisms.
The arrows on the Enneagram point in the direction of integration towards the type individuals can look to for growth.
For example, a Type Nine (the Peacemaker) shows growth by moving towards Type Three (the Achiever), indicating they become more self-developing, energetic, and goal-oriented in positive ways.
Recognizing these pathways can inspire individuals to pursue traits and behaviors that foster personal development and well-being.
The concepts of arrows and connecting lines underscore the fluidity and dynamic nature of the Enneagram personality system. They remind us that our personalities are not fixed, while we have a primary type.
We can move along these pathways in both positive and negative directions depending on our level of awareness, circumstances, and efforts toward growth. It’s a call to be mindful of our behaviors and to actively work on adopting the healthier aspects of our integration points.
In practical terms, working with arrows and connecting lines encourages a proactive approach to personal development. By being aware of the signs of stress and recognizing the growth opportunities, individuals can consciously work towards embodying the positive traits of their integration points.
This may involve setting specific goals, engaging in new activities, or simply adopting a more mindful approach to self-reflection and interaction with others. Ultimately, it fosters a more balanced, integrated, and fulfilling life.
Subtypes
The Enneagram’s complexity deepens with the exploration of subtypes, which provide a more nuanced understanding of each personality type. These subtypes are influenced by the dominant instinctual drives: self-preservation, social, and sexual (one-to-one) instincts.
Each type uniquely expresses these instincts, offering a broader spectrum of behaviors and motivations within the same type.
This layer of complexity allows individuals to identify more closely with their type, recognizing the specific ways in which their basic fears and desires manifest in daily life.
Self-preservation subtypes focus on personal safety, comfort, and well-being. This subtype is concerned with managing resources, ensuring physical health, and maintaining environmental security.
In the context of personal development, understanding one’s self-preservation subtype can highlight areas of excessive caution or self-neglect, guiding individuals towards healthier behaviors that promote physical and emotional well-being.
Social subtypes emphasize interpersonal relationships and community involvement. People with a dominant social instinct are keenly aware of their roles within groups, strive for acceptance, and often prioritize the community’s needs above their own.
Identifying with a social subtype can shed light on one’s social behaviors, encouraging growth in engaging with others more authentically and fostering meaningful connections.
The sexual (one-to-one) subtype drives individuals to seek out intensity, intimacy, and close personal connections. This pursuit often manifests as a deep desire for connection with a significant other or a passion for activities that elicit strong emotional responses.
For individuals identifying with this subtype, personal development can involve balancing this intensity with different aspects of life, ensuring that pursuing passion supports, rather than detracts from, overall life goals.
Understanding subtypes within the Enneagram provides a comprehensive tool for self-reflection and growth.
By recognizing where one’s instinctual drives are most pronounced, individuals can tailor their development efforts more effectively, working to balance their instincts in a way that supports a fulfilling and balanced life.
The Levels of Development
Understanding the Enneagram’s Levels of Development provides a nuanced view of personal growth. These levels describe how behaviors and motivations change as individuals become more self-aware and emotionally healthy or less so.
The spectrum ranges from healthy, average, to unhealthy, depicting a person’s psychological state and capacity for empathy, reflection, and self-control.
At healthy levels, individuals exhibit qualities of self-actualization and fulfillment. They are more self-aware, empathetic, and balanced in their approach to life’s challenges. For those identifying with the self-preservation subtype, this might mean balancing caution and risk-taking.
Social subtypes at healthy levels are adept at forming meaningful relationships without losing individuality. The sexual (one-to-one) subtype, in this state, maintains intense relationships without overshadowing other life aspects.
Average levels reflect a state where individuals often operate on autopilot, guided by their instinctual drives without much introspection. Self-preservation subtypes may oscillate between self-care and neglect, struggling to balance.
Social subtypes might be overly conforming to group norms or dissatisfied with their social standing. For the sexual (one-to-one) subtype, there’s a continuous search for intimacy, sometimes at the cost of other valuable connections or personal development.
At unhealthy levels, individuals may experience significant distress, manifesting behaviors that can be self-destructive or harmful to others. Self-preservation subtypes might become overly paranoid about their safety or completely neglectful.
Social subtypes could withdraw entirely from social interactions or become overly manipulative in their quest for belonging. The sexual (one-to-one) subtype might engage in dangerously intense relationships or exhibit extreme emotional volatility.
When combined with the instinctual subtypes, these developmental levels furnish a comprehensive framework for understanding human behavior.
They illustrate how varying degrees of psychological health affect one’s actions and interactions with the world. By reflecting on their level of development, individuals can pinpoint areas for growth and work towards a more integrated and balanced self.
History of the Enneagram
The Enneagram is an ancient system that maps human personality into nine primary types. It’s believed to have roots in several spiritual and philosophical traditions, spanning from mystic Sufism to Christian mysticism, though its exact origin is unclear.
The modern Enneagram of Personality that we’re familiar with today was developed in the 20th century, incorporating psychological aspects with these ancient teachings to aid personal and spiritual development.
Enneagram comes from the Greek words ‘ennea’ (nine) and ‘grammos’ (figure), reflecting its symbol of a nine-pointed figure. Historically, the Enneagram symbol is thought to have been used for spiritual guidance, representing the circle’s unity, the Head’s dynamism, and the triangle’s change.
Its transformation into a tool for understanding personality types is credited to several key figures, including George Gurdjieff, a spiritual teacher who introduced the Enneagram figure to the West in the early 20th century.
However, Gurdjieff did not associate the Enneagram with personality types, using it as a cosmic symbol.
The shift towards the psychological application of the Enneagram began with Oscar Ichazo in the 1950s and 1960s. Ichazo, the founder of the Arica School, identified specific ego fixations, fears, and desires with each of the nine points, thus laying the groundwork for the Enneagram of Personality.
Claudio Naranjo, a Chilean psychiatrist, further expanded on Ichazo’s teachings, integrating them with modern psychology and bringing them to the attention of the academic and therapeutic communities in the 1970s.
Naranjo’s efforts were instrumental in elucidating the connection between the Enneagram types and various psychological states and behaviors.
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, the Enneagram gained growing recognition within various fields, including psychotherapy, business, and spirituality. Books and workshops proliferated, offering insights into personal growth, interpersonal relationships, and organizational development.
The system’s nuanced approach to understanding personality traits and motivations – beyond mere categorization – appealed to those seeking deeper self-knowledge and more effective ways to relate to others.
The role of instinctual subtypes in refining the understanding of each primary type underscored the Enneagram’s complexity and adaptability. Mapping these subtypes onto the three basic instincts – self-preservation, social, and sexual (one-to-one) – enriched the explanatory power of the Enneagram.
This layer added a dynamic dimension to the types, illustrating how primary motivations and concerns could vary significantly within the same personality type.
As the Enneagram continues to evolve, practitioners and scholars contribute to expanding its teachings and applications. Integrating developmental levels into the Enneagram framework marks a significant advancement in its psychological precision.
This has made the Enneagram a valuable tool for personal and spiritual growth, professional development, and counseling. Its history reflects a rich tapestry of philosophical and spiritual wisdom intertwined with the pursuits of modern psychology.
Uses and Applications of the Enneagram
With its rich layers of psychological insight, the Enneagram system finds its applications across diverse areas, including personal growth, team building, conflict resolution, and leadership development.
Individuals leverage the Enneagram to unearth deep-seated motivations, fears, and desires in personal growth.
By identifying their Enneagram type, individuals gain clarity about their behavioral patterns and the underlying emotional triggers, setting the stage for profound self-awareness and transformation.
The Enneagram acts as a mirror, reflecting the intricacies of an individual’s personality. This reflection guides people in understanding their strengths and weaknesses, often illuminating paths to personal development.
For instance, recognizing the type-specific coping strategies can help individuals confront and overcome habitual reactions that impede personal growth.
Furthermore, the knowledge of instinctual subtypes enables individuals to address more nuanced aspects of their behavior and relationships, enhancing emotional intelligence and social skills.
Businesses and organizations employ the Enneagram for team building and leadership development. Understanding the diverse Enneagram types within a team can foster empathy and appreciation among members, reducing conflict and enhancing collaboration.
Leaders trained in Enneagram principles can adapt their communication and motivational strategies to suit the distinctive needs of their team members, thereby improving management effectiveness and organizational productivity.
Additionally, the Enneagram’s insights into stress and growth points for each type can be instrumental in designing personalized professional development plans.
Therapists and counselors use the Enneagram as part of their therapeutic toolkit to better understand clients and tailor interventions. The system’s depth facilitates a nuanced grasp of clients’ personality structures, offering clues to the psychological roots of their issues.
This understanding allows therapists to connect with clients on a deeper level and guide them more effectively through the healing process.
The developmental aspect of the Enneagram, with its focus on growth and integration, provides a hopeful framework for clients, emphasizing the potential for positive change and self-improvement.
The Enneagram stands out for its adaptability and depth in every use case. It can serve as a guide for personal evolution, a framework for enhancing interpersonal dynamics, or a tool for professional growth.
Its emphasis on self-discovery and development remains a central element, irrespective of the context in which it is applied.
By fostering an understanding of diverse personality types and their interplay, the Enneagram promotes a more compassionate and functional approach to dealing with the complexities of human behavior and relationships.
Enneagram FAQ
Why is the Enneagram useful?
The Enneagram is incredibly useful because it offers a deep and nuanced understanding of personal and professional development.
At its core, it is more than just a personality typing system. It’s a roadmap for growth, self-awareness, and understanding others, which is fundamental in personal and professional contexts.
Its precision in identifying different personality types’ core motivations, fears, and desires can profoundly impact how individuals engage with their environment and those around them.
One of the Enneagram primary benefits of Enneagram is its ability to enhance self-awareness. You gain insight into your core motives, fears, and overall worldview by pinpointing your primary Enneagram type. This recognition is the first step toward growth, providing clear direction for personal development.
The Enneagram also outlines specific growth paths for each type, offering practical steps for overcoming obstacles and achieving a more integrated and fulfilled self.
The Enneagram also plays a crucial role in improving interpersonal relationships. Understanding your Enneagram type and the types of those you’re close to can significantly improve the way you communicate and relate with each other.
By recognizing and appreciating different types’ unique perspectives and values, individuals can foster deeper connections, reduce conflicts, and support one another’s growth in thoughtful, personalized ways.
How do I know my Enneagram type?
Determining your Enneagram type is an insightful voyage into your inner workings, guiding you toward profound self-awareness. Start by engaging with reputable Enneagram tests that are available online. These questionnaires, designed by Enneagram experts, can offer a preliminary insight into your dominant type.
However, remember that these results are just a starting point. The true essence of the Enneagram transcends a mere questionnaire; it’s about recognizing yourself in the rich descriptions of each type’s motivations, fears, and worldview.
After your initial assessment, immerse yourself in the comprehensive descriptions of your suggested types. This is where the Heart of the Enneagram’s work lies. It’s common to see aspects of yourself in multiple types; however, your core type will resonate with your deepest motivations and fears.
Engage with Enneagram books, workshops, and courses that offer a more nuanced exploration of the types. Listening to the experiences of others who identify with your type can also illuminate, as it brings the descriptions to life through real-world applications and examples.
Once you fully grasp your main Enneagram type, consider exploring your wings and subtypes. Wings are the numbers adjacent to your core type on the Enneagram diagram, and they can influence your personality, adding layers to your primary type’s characteristics.
Subtypes, determined by dominant instinctual energies (self-preservation, sexual, or social), further refine your core type’s expression. This deeper exploration enriches your understanding of yourself, clarifying your behaviors and motivations.
Why is it called Enneagram?
It is called Enneagram because it is based on a geometric figure with nine points and lines connecting them. Ennea means nine in Greek, and gram means drawing or diagram.
The origins of the Enneagram are traced back to ancient traditions, including Sufism, Kabbalah, and Christianity. However, it was not until the 20th century that the modern understanding of the Enneagram as a personality typing system emerged.
Today, the Enneagram is widely used for personal growth and development and in business settings for team-building and leadership training. It offers a unique perspective on human behavior and motivations, providing individuals with a framework to understand themselves and others better.
One of the key concepts in the Enneagram is that each person has a dominant personality type, represented by one of the nine points on the diagram. The types are numbered 1 through 9 and are connected by lines representing how each type relates to the others.
Each type has its own set of traits, strengths, weaknesses, and motivations. For example, Type One is often described as principled, responsible, and perfectionistic, while Type Nine is known for being easy-going, supportive, and adaptable.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Enneagram serves as a potent tool for self-discovery and personal growth, guiding individuals through the intricate layers of their personalities.
By understanding your primary type, exploring your wings and subtypes, engaging with the Enneagram community, and applying this knowledge daily, you can achieve a deeper self-awareness and more fulfilling life.
The journey through the Enneagram is ongoing and dynamic, reflecting human identity’s complex and evolving nature. With dedication and openness, this path can lead to profound insights and transformations, enriching your understanding of yourself and your relationships with others.


